
The shoe protects the foot from the roughness of the ground and climatic variations. Despite this, the foot is subject to significant physical stresses: it ensures balance in a static position, allows movement over various terrain, flat or uneven, up and down stairs, and responds to spontaneous acceleration.
During an activity, the shoe must respect the movements of the foot: it must neither oppose, nor promote or amplify its natural movements.
All of these consumer expectations for a shoe are incorporated by the manufacturer into what we call the fit. The footwear will be defined by the design office, and described in the functional specifications of the product. This integrates the specific needs related to the individual and the activity.
To be comfortable to wear, the shoe must best match the shape of the foot, but must also meet the requirements of the activity for which it is intended. There is thus a great diversity of ranges of shoes. We find the ranges segmenting the ages (child, woman, man and senior shoe), or the shoes classified by activity (sports shoe, safety shoe, etc.).
The consumer cannot imagine the number of operations necessary to make a shoe, from the thought of the stylist or designer, to putting the finished products in the store. Indeed, this process sees the intervention of a multitude of know-how, as well as a collaboration of the manufacturer with many suppliers.
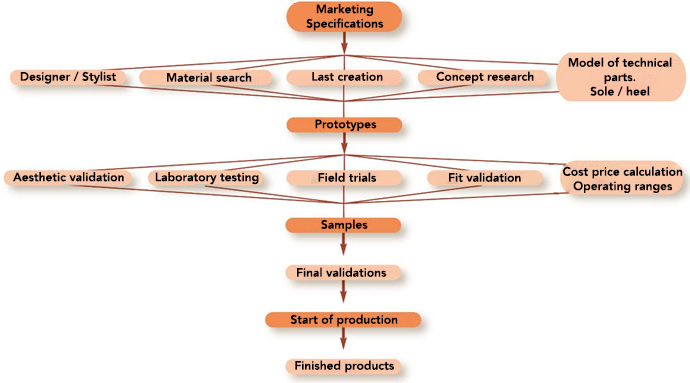
Shoe manufacturing flowchart
There are several steps to creating a shoe:
|
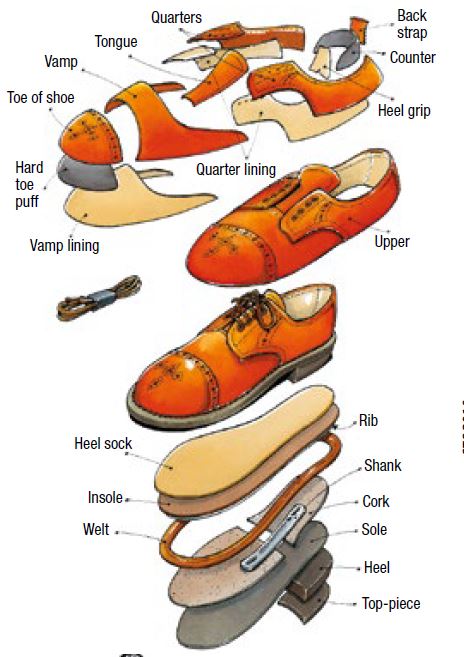
A shoe can be broken down into three main parts:
To create, assemble and format these three elements, you must first create a fourth element: the last. The volume of the last approaches that of the foot. |
CTC, professional economic development committee for the footwear, leather goods, gloves and leather fashion sector, is the privileged interlocutor for all production, design, quality control and innovation issues in the footwear sector. The scope of our services affects all stages in the life of a shoe, from specifications to recycling.
CTC recommends a series of basic tests in order to be able to qualify and evaluate the shoe. Here is the recommended test pack below.
|
RECOMMENDED TESTS |
||
|
Component |
Test designation |
Standard |
|
TOP |
Tear Resistance |
ISO 17696 |
|
LINING |
ISO 17700 |
|
|
OUTSOLE |
Flexural strength |
EN ISO 17707 |
|
Abrasion resistance |
EN 12770 |
|
|
FULL SHOE |
Resistance of upper / sole adhesion |
EN ISO 17708 |
|
HEEL |
CTC Method CTC-P-CH-016 |
|
These additional tests are carried out on the different components of the shoe. The test that we recommend is carried out in accordance with a French, European or international standard.
Select the component to find out the corresponding tests and standards:
| Designation of the test | Standard |
| Legal information | DIR 94-11 CEE |
| Designation of the test | Standard |
|
Tear resistance |
ISO 17696 |
|
Tensile strength and elongation at break |
ISO 17706 |
|
NF EN ISO 17694 |
|
|
Resistance of stopping points |
NF G62.013 |
|
ISO 17700 |
|
|
Water resistance (penetration) |
ISO 17702 |
|
Determination of permeability and absorption of water vapor |
EN 13515 |
|
Determination of animal species |
Microscope |
| Designation of the test | Standard |
|
Tear resistance |
ISO 17696 |
|
Tensile strength and elongation at break |
ISO 17706 |
|
NF EN ISO 17694 |
|
|
Resistance of stopping points |
NF G62.013 |
|
ISO 17700 |
|
|
Water resistance (penetration) |
ISO 17702 |
|
Determination of permeability and absorption of water vapor |
EN 13515 |
| Designation of the test | Standard |
|
Tear resistance |
ISO 17696 |
|
Abrasion resistance |
EN 13520 |
|
ISO 17700 |
|
|
Determination of permeability and absorption of water vapor |
EN 13515 |
| Designation of the test | Standard |
|
ISO 17700 |
|
|
Determination of water absorption capacity |
EN ISO 22649 |
| Designation of the test | Standard |
|
Flex resistance |
EN ISO 17707 |
|
Flex resistance (small size) |
ISO 132 |
|
Abrasion resistance |
EN 12770 |
|
Determination of density |
EN 12770 |
|
Resistance to tensile strength and elongation |
EN 12803 |
| Designation of the test | Standard |
|
Top piece retention strength |
EN ISO 19958 |
|
Abrasion resistance |
EN 12770 |
|
Abrasion resistance |
LHOMARGY |
| Designation of the test | Standard |
|
CTC method |
| Designation of the test | Standard |
|
Abrasion resistance of shoe laces |
ISO 22774 |
|
Side opening resistance of zipper |
BS 3084 |
|
Aging zips |
BS 3084 |
|
Touch and close fasteners shear strength |
EN ISO 22777 |
|
Accessories tear strength |
EN 71-1 |
|
Metallic accessories corrosion resistance |
CTC méthode |
| Designation of the test | Standard |
|
Determination adhesion between outsole and upper |
EN ISO 17708 |
|
Determination adhesion between midsole and outsole |
EN ISO 17708 |
|
Determination of washability in domestic washing machine |
EN ISO 19954 |
|
Flex resistance whole shoes (wear simulation) |
CTC Method |
| Designation of the test | Standard |
|
Shock absorption on the heel (cushioning) |
CTC Method |
|
Energy return on the heel |
CTC Method |
|
Determination of the suppleness |
CTC Method |
|
Assessment of sole correction properties in the heel area (supination/pronation) |
CTC Method |
|
Impact resistance of stud |
CTC Method |
|
Determination of the torsional moment in the waist area |
CTC Method |
|
Assessment of the heel seat side carriage |
CTC Method |
|
Heat abrasion resistance |
CTC Method |
|
Water resistance of footwear |
CTC Method |
|
Cold insulation |
EN ISO 20344 |
|
Resistance of outsole after compression cycles (walking) |
CTC Method |
|
Resistance of outsole after compression cycles (running) |
CTC Method |
|
Water vapor permeability of whole footwear |
CTC Method |
| Color legend | |||
| Mechanical properties | Color fastness | Hygienic comfort | Other |
Need information or a quote, CONTACT
CONTACT